A term used to describe the process of economic expansion (positive output gap) and contraction (negative output gap) that economies experience over time.
Below is a depiction of the theoretical movement of a country's economic cycle. What this diagram is showing is that an economy typically moves from periods of growth, and this culminates in a boom (peak). After this the economy hits a downturn, as economic growth cannot be sustained. If the downturn is sustained for more than two quarters this creates an economic recession, in which the economy hits a trough (the lowest point of growth). Eventually an economy will arrest the decline in growth, as a result of economic policies, and this enables the economy to recover over time. After which, the whole economic cycle restarts.
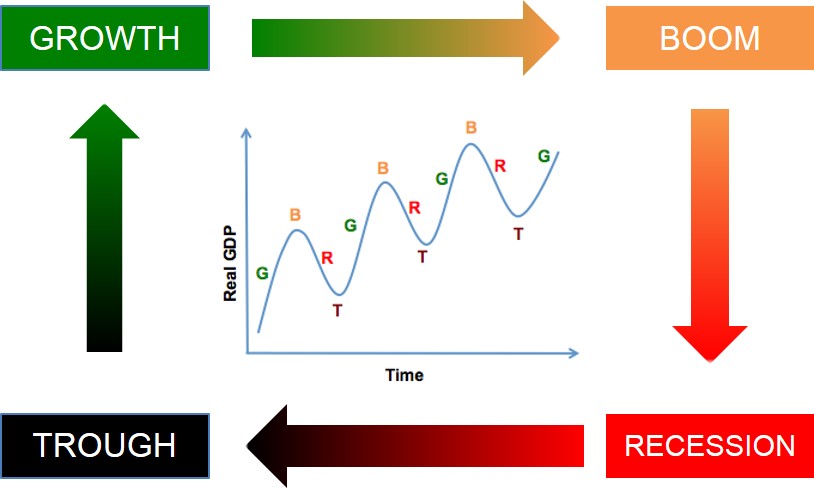
It is important to appreciate that the depth and duration of cycles and phases within the cycle will vary considerably due to individual specifics within each country (as well as external influences) and therefore a country's economic cycle will not always match the smooth shape of the economic cycle above.