UK goods that are sold to other countries - any transaction that generates a positive monetary flow into the UK e.g. Land Rover cars sold abroad or foreign money flowing into the UK financial services industry.
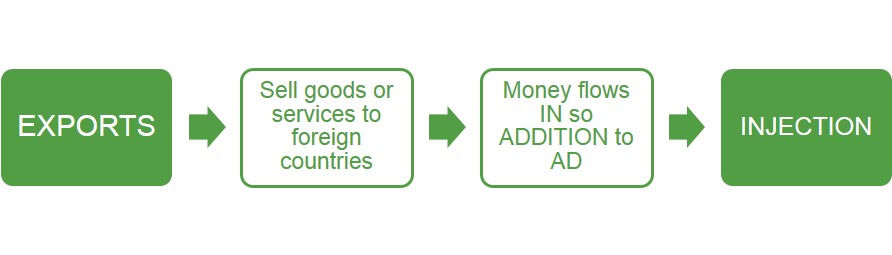
Below is a diagram to show that exports represent an injection into a country's circular flow of income as it is money from other countries being spent on domestically produced goods.
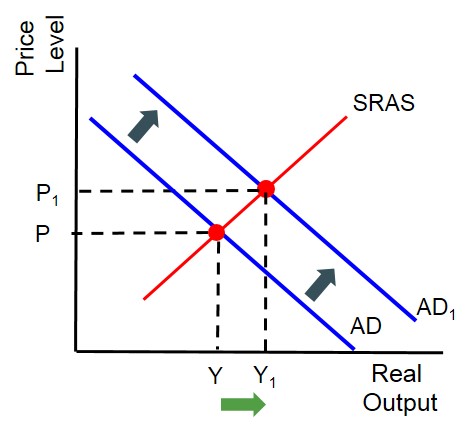
Therefore exports contribute to the aggregate demand curve and if exports increase due to a weaker pound sterling then it will cause the AD curve to shift outwards as shown in the diagram below.