This is a type of collusion in which formal and explicit co-operation and agreements take place between rival firms. This type of collusion normally leads to a cartel forming amongst firms.
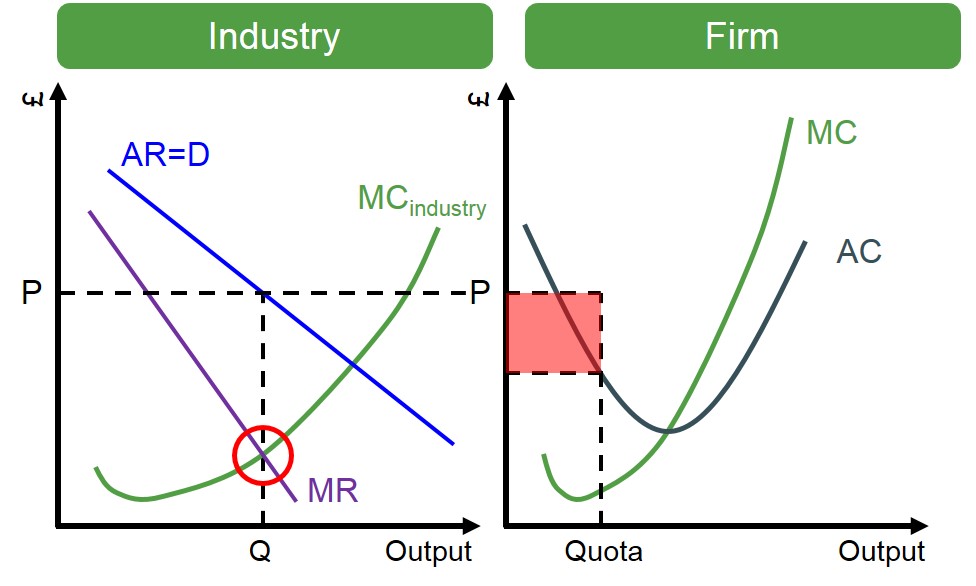
The diagram below shows the individual and market outcome of this form of collusion. In this instance, if all firms charge a price of P, ths leads to all firms producing a fixed quota of goods making a level of supernormal profit equal to the red shaded box below. Therefore, this ensures that industry profits are maximised.