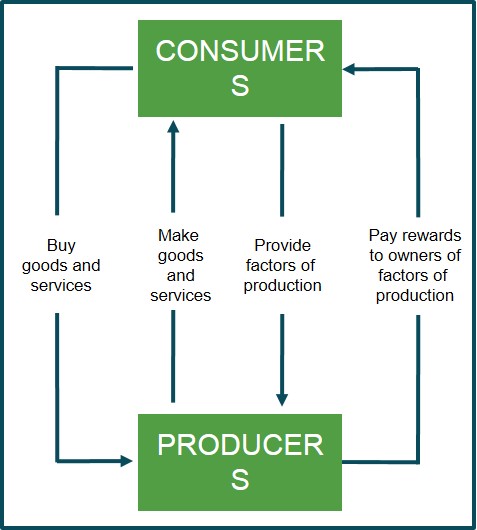
The process by which expenditure generates a trail of subsequent expenditure so that the resultant change in national income will exceed the amount initially expended.
Below is a diagram to show how the mulitplier effect in an a economy is realised. For instance if there was an increase in investment from a firm to increase the size of the office by £1million, this would lead to a greater than £1million increase in aggregate demand due to the multiplier. Firstly that £1million would go to the building company in charge of expanding the office, who would then use that money to pay for the nominal wages of the individual builders in charge of the project. This would then make up part of worker's disposable income and this would be spent on consumer goods such as food and clothes. All this extra spending would contribute towards a higher level of national income.