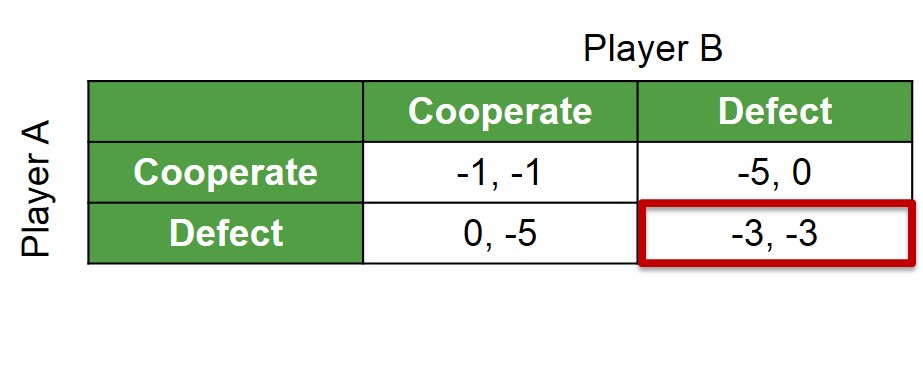
A situation analysed using game theory that shows why two rational individuals might not cooperate, despite it being in their best interests to do so.The Nash Equilibrium in this game will always be for both players to betray each other despite the payoffs for both players being higher if they were willing to cooperate. This game is based on the idea of two prisoners who have committed a crime with an adverse feeling towards years in prison.
Below is a payoff matrix to illustrate the equilibrium concept of the game.