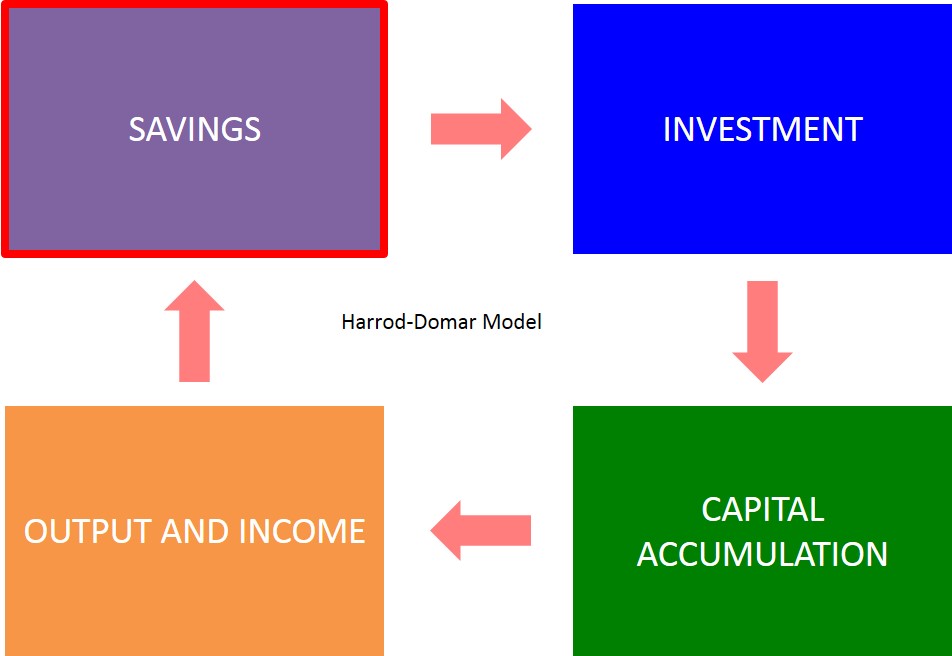
Is a growth model used in development economics that states an economy's growth rate is dependant on the level of saving and the capital output ratio. The theory states that developing countries have very low growth rates and therefore the standard of living does not advance rapidly, because of the fact that they have very low levels of saving and each unit of capital is very inefficient.
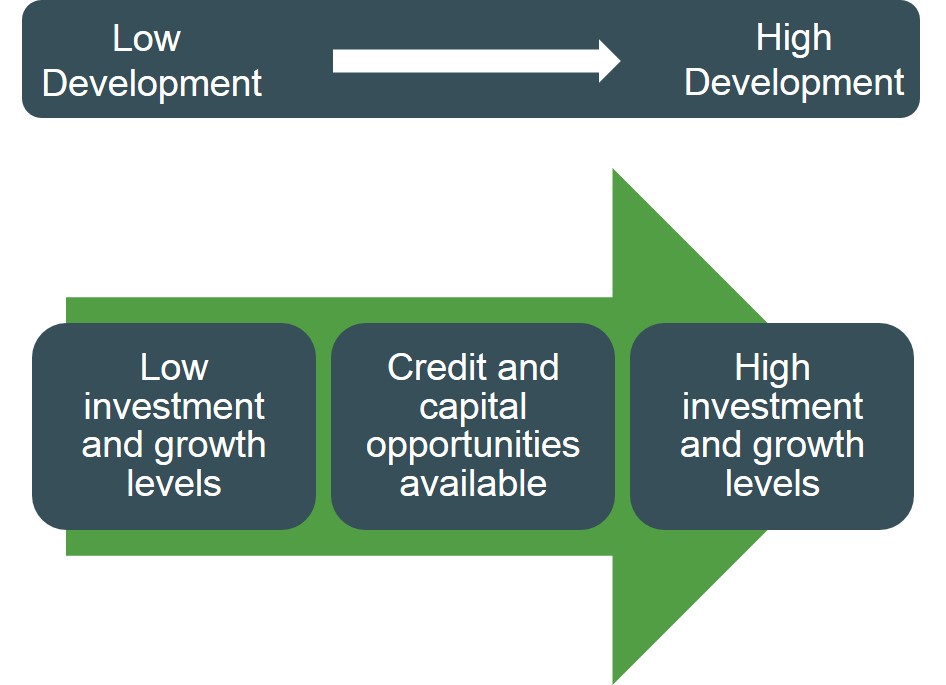
Below is a logical sequence of reasoning to illustrate that the more developed a country wants to be and the quicker the economy will grow is based on investment levels in infratructure products.
Here is a basic flowchart of how the HD model works. Countries with high savings rate will then provide lots of funds for investment for firms to increase the capital stock for a country and this in turn will lead to an increase in the growth rate of a country and as a result the level of national income/output will increase fuelling further savings and ultimately this cycle wil keep repreating itself.